Physical vapor deposition of zirconium or titanium thin films on flexible polyurethane highly support adhesion and physiology of human endothelial cells.
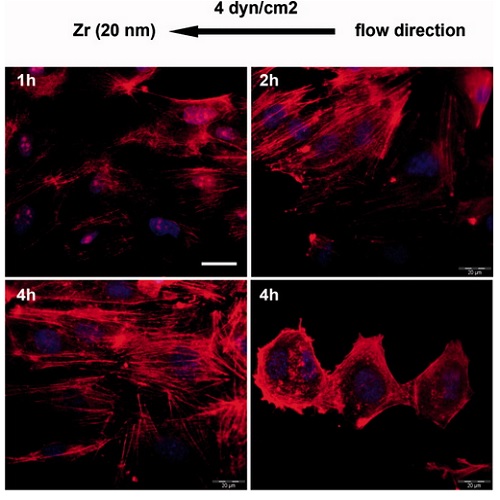
The aim of this study was to develop and characterize novel metal-polymer constructs to improve the biocompatibility of flexible but hydrophobic polyurethane (PUR) implants. Using a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique, thin films (< or =100 nm) of zirconium (Zr) or titanium (Ti) were deposited on the polyurethane surface. Both coatings displayed good stability when subjected to cross-cutting test and especially Zr showed only minor and superficial cracks in the scanning electron microscopy analysis. PVD coating resulted in significantly lowered contact angles and the standard surface free energy of wetting (Delta(wet)G degrees ) turned to more favorable negative values (Ti: -40; Zr: -30; untreated PUR (uPUR): +10.1 mN/m). This may lead to the highly enhanced adhesion and proliferation properties observed with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In addition, the novel coatings had no toxic effect and even drastically reduced apoptosis rates of HUVECs. Cell morphology, nitric oxide production, and mitochondrial membrane potential--both at static and flow conditions--were superior compared with uPUR, thus demonstrating intact physiological functions. Therefore, we suggest that combining PUR as a flexible material with a thin coating of Zr or Ti as the improved biocompatible surface may have advantages for use, for example, vascular graft material.
- J Biomed Mater Res A 2009 Apr;89(1):57-67
- 2009
- Medical Biology
- 18404717
- PubMed
Enabled by:
