Cortical domain correction repositions the polarity boundary to match the cytokinesis furrow in C. elegans embryos.
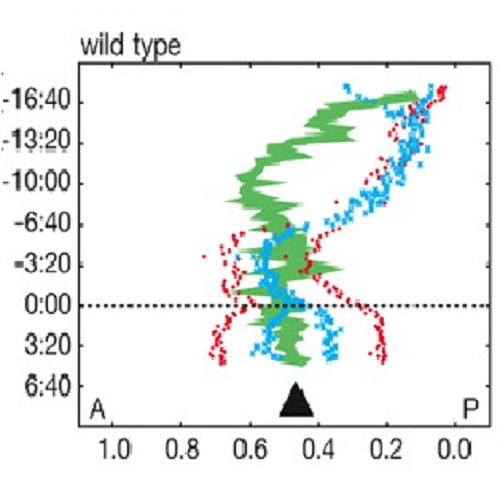
In asymmetrically dividing cells, a failure to coordinate cell polarity with the site of cell division can lead to cell fate transformations and tumorigenesis. Cell polarity in C. elegans embryos is defined by PAR proteins, which occupy reciprocal halves of the cell cortex. During asymmetric division, the boundary between the anterior and posterior PAR domains precisely matches the site of cell division, ensuring exclusive segregation of cell fate. The PAR domains determine the site of cell division by positioning the mitotic spindle, suggesting one means by which cell polarity and cell division might be coordinated. Here, we report that cell polarity and cell division are coordinated through an additional mechanism: the site of cell division repositions the PAR-2 boundary. Galpha-mediated microtubule-cortex interactions appear to direct cortical flows of PAR-2 and myosin toward the site of cell division, which acts as a PAR-2 and myosin sink. Embryos with defects in PAR-2 boundary correction undergo mis-segregation of cortical polarity and cytoplasmic determinants, suggesting that PAR domain correction might help prevent cell fate transformation.
- Development 2010 May;137(10):1743-53
- 2010
- Developmental Biology
- 20430749
- PubMed
Enabled by:
