Release of extracellular membrane vesicles from microvilli of epithelial cells is enhanced by depleting membrane cholesterol.
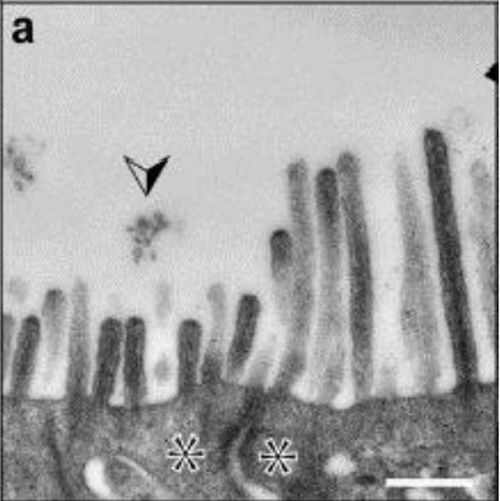
We previously reported on the occurrence of prominin-1-carrying membrane vesicles that are released into body fluids from microvilli of epithelial cells. This release has been implicated in cell differentiation. Here we have characterized these vesicles released from the differentiated Caco-2 cells. We find that in these vesicles, prominin-1 directly interacts with membrane cholesterol and is associated with a membrane microdomain. The cholesterol depletion using methyl-beta-cyclodextrin resulted in a marked increase in their release, and a dramatic change in the microvillar ultrastructure from a tubular shape to a "pearling" state, with multiple membrane constrictions, suggesting a role of membrane cholesterol in vesicle release from microvilli.
- FEBS Lett. 2009 Mar 4;583(5):897-902
- 2009
- Cell Biology
- 19302789
- PubMed
Enabled by:
